Web Developer: Qualifications and Responsibilities
Web Developer: Skills, Roles & Career Guide
In today’s digital age, web development has become one of the most in-demand careers, offering unprecedented opportunities for growth and innovation. As companies worldwide race to establish their digital presence, demand for skilled web developers continues to rise. Whether you’re a recent graduate, a career changer, or simply passionate about technology, becoming a web developer opens doors to a world of creativity, problem-solving, and financial stability.
Digital transformation has made the web developer role not just a career option but a gateway to shaping the future. From e-commerce platforms revolutionizing shopping experiences to social networks connecting billions of people across the globe, web developers are the architects behind these digital marvels. As a web developer, you’ll find yourself at the forefront of technological advancement, devising solutions that impact millions of users every day.
This comprehensive guide will take you through everything you need to know about becoming a successful web developer—from core qualifications to day-to-day responsibilities, career paths, and future outlook. You’ll discover the most essential skills, your available education options, and the practical steps you can take to start your path in this exciting field.
What Is a Web Developer and Their Core Role
A web developer is a technology professional who specializes in creating, building, and maintaining websites and web applications. Your role as a web developer extends far beyond simply writing code—you become a digital architect, a problem-solver, and a user-experience artisan all in one. You’ll work with various programming languages, frameworks, and tools to bring ideas to life on the internet.
The distinctions between web developers and web designers are critical to understand. While web designers focus primarily on visual aspects and user-interface design, web developers concentrate on functionality, performance, and technical implementation. As a web developer, you translate initial designs into fully functional websites that users can interact with seamlessly.
Web developers play a vital role in modern businesses and organizations. You will be responsible for creating the online storefront that represents companies on the web, developing applications that enhance workflow, and ensuring sites run at peak efficiency across different devices and browsers. Your work directly influences how customers interact with brands and how efficiently business operations run in the digital space.
This profession has evolved significantly over the years, adapting to new technologies, user expectations, and business requirements. What began as simple static HTML pages has transformed into interactive, complex web applications that rival traditional desktop software in functionality and user experience.
Types of Web Developers and Different Specializations
Front-End Developer Specialization
As a front-end developer, you’ll focus on the client side of web development—everything users see and interact with directly. Your responsibilities include creating responsive layouts, implementing interactive features, and ensuring an optimal user experience across different devices and browsers. You’ll work extensively with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, along with modern frameworks such as React, Angular, and Vue.js.
Front-end development requires a sharp eye for design and strong attention to detail. You’ll collaborate closely with UX/UI designers to translate visual concepts into functional code, optimize sites for performance and accessibility, and ensure cross-browser compatibility. Your responsibilities involve understanding user behavior and building interfaces that are both visually engaging and highly functional.
Back-End Developer Specialization
Back-end development is about working with the server-side components that power websites and applications. As a back-end developer, you’ll manage databases, create APIs, handle server configuration, and ensure data security. Your work remains invisible to end users but forms the foundation that makes everything else possible.
You’ll work with programming languages such as Python, Java, PHP, Ruby, and Node.js, along with database management systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. Back-end developers must understand server architecture, security protocols, and performance-optimization techniques to build robust, scalable web applications.
Full-Stack Developer Path
Full-stack developers possess comprehensive knowledge of both front-end and back-end technologies. As a full-stack developer, you’ll have the flexibility to work on complete web projects from concept to deployment. This specialization demands broader knowledge across multiple technologies and the ability to understand how different components of web applications interact with one another.
Full-stack web development offers greater career flexibility and often comes with higher compensation due to the comprehensive skill set required. You’ll be able to work independently on small projects or lead development teams on larger initiatives, making strategic decisions about technology choices and system architecture.
Core Technical Qualifications for Web Developers
Programming Language Fundamentals
Your success as a web developer depends heavily on mastering the core programming languages of web development. HTML and CSS form the cornerstone of the web, providing the structure and styling for web pages. These markup and styling languages are essential regardless of your specialization, as they determine how content appears and behaves in browsers.
JavaScript has become indispensable in modern web development, enabling interactive features and dynamic content on websites. As a web developer, you’ll use JavaScript for everything from simple form validation to complex single-page applications. A strong understanding of JavaScript opens doors to both front-end and back-end opportunities.
For back-end development, you’ll need proficiency in at least one server-side programming language. Python is popular for its simplicity and versatility; PHP powers a large portion of the web, including WordPress; Java provides enterprise-grade capabilities; while Ruby offers elegant syntax for rapid development. Your choice often depends on project requirements, company preferences, and personal inclinations.
Mastering Frameworks and Libraries
Modern web development relies heavily on frameworks and libraries that accelerate development and provide standardized solutions to common problems. React, Angular, and Vue.js dominate front-end development, each offering a different approach to building user interfaces. Learning at least one of these frameworks significantly increases your employability and development efficiency.
Back-end frameworks such as Django for Python, Laravel for PHP, Express.js for Node.js, and Ruby on Rails offer structured approaches to server-side development. These frameworks come with built-in security features, database-management tools, and architectural patterns that make development more efficient and maintainable.
Understanding how to work with CSS frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS speeds up front-end development and ensures responsive design across devices. These frameworks provide prebuilt components and grid systems that let you create professional-looking websites quickly.
Database Management Skills
Every web application needs to store and retrieve data efficiently. As a web developer, you should understand both SQL and NoSQL database systems. SQL databases such as MySQL and PostgreSQL provide structured data storage with powerful querying capabilities, while NoSQL databases like MongoDB offer flexible document storage for modern applications.
Your database-management skills should include designing efficient database schemas, writing optimized queries, understanding indexing strategies, and implementing necessary backup and security procedures. These skills are vital for building scalable applications that can handle increasing amounts of data and users.
Required Education and Certifications
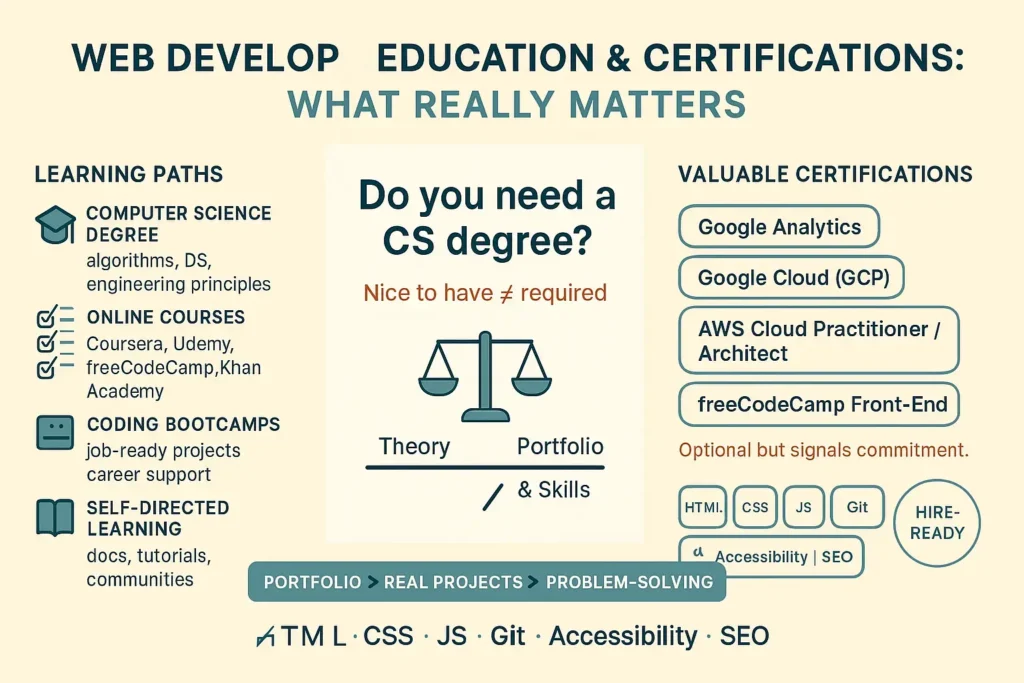
Do You Need a Computer Science Degree?
The beauty of web development lies in its accessibility—you don’t necessarily need a formal computer science degree to succeed in this field. While a degree can provide a strong theoretical foundation and may be preferred by some employers, many successful web developers are self-taught or have completed alternative education programs.
What matters to employers is your ability to build well-designed, functional websites and applications. Your portfolio, hands-on experience, and problem-solving skills often carry more weight than formal credentials. That said, a computer science degree can offer valuable knowledge in algorithms, data structures, and software engineering principles that enhance your development capabilities.
Alternative Learning Paths
Online courses have revolutionized web-development education by offering flexible, affordable learning options. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, freeCodeCamp, and Khan Academy provide comprehensive web-development curricula taught by industry professionals. These courses typically include practical projects you can add to your portfolio.
Coding bootcamps provide intensive, hands-on training designed to prepare you for web-development careers in months rather than years. These programs focus on job-ready skills and often include job-search support. Although bootcamps require significant time and financial investment, they can accelerate your entry into the field.
Self-directed learning remains a viable path for highly motivated individuals. With abundant free resources online—including documentation, tutorials, and community forums—you can build a well-rounded web-development skill set on your own. This approach requires strong self-discipline and the ability to structure your learning path.
Valuable Professional Certifications
While certifications aren’t always mandatory, they can demonstrate your commitment to professional development and validate your skills to potential employers. Google offers various certifications, including Google Analytics and Google Cloud Platform credentials, which are valuable for web developers working with data and cloud services.
AWS (Amazon Web Services) certifications are especially valuable if you work with cloud infrastructure. These credentials showcase your ability to build and deploy scalable web applications using industry-standard cloud platforms.
Front-end development certifications from organizations like freeCodeCamp provide structured learning paths and verifiable credentials. These certifications often require completing multiple projects, giving you practical experience alongside theoretical knowledge.
Core Responsibilities of Web Developers
Designing and Developing Websites
As a web developer, your primary responsibilities involve transforming client requirements and design concepts into functional websites and web applications. This process begins with analyzing project requirements, understanding user needs, and planning the technical architecture. You’ll create wireframes and prototypes that outline structure and functionality before diving into actual development.
The development phase demands close attention to coding standards, best practices, and performance optimization. You’ll write clean, maintainable code that other developers can easily understand and modify. This requires consistent naming conventions, appropriate code comments, and organizing files into logical structures.
Coding and Maintenance
Writing code is only the beginning of your responsibilities. Maintaining and updating existing codebases consumes a substantial portion of your time. You’ll fix issues, implement new features, and refactor code to improve performance and maintainability. Ongoing maintenance ensures websites continue to function correctly as browsers, devices, and user expectations evolve.
Quality assurance is an essential part of maintenance. You’ll conduct thorough testing across different browsers and devices, identify and fix bugs, and ensure all features work as expected. This includes implementing automated tests where appropriate and following version-control best practices to track changes and collaborate effectively with team members.
Website Performance Optimization
Modern users expect fast load times and smooth performance across all devices. As a web developer, you’ll optimize images, reduce HTTP requests, implement caching strategies, and fine-tune code to achieve quick load times. Performance optimization directly affects user experience and search engine rankings.
SEO considerations should be integrated into your development process. You’ll implement semantic HTML, optimize meta tags, ensure mobile responsiveness, and structure content for search engine crawlers. Understanding SEO principles helps ensure the sites you build can be discovered and rank well in search results.
Implementing and Maintaining Security
Website security is a critical responsibility you cannot overlook. You’ll implement security best practices, including input validation, SQL-injection prevention, XSS protection, and secure authentication mechanisms. Understanding common vulnerabilities and how to prevent them is essential for protecting user data and maintaining trust.
Regular security updates and monitoring are part of your ongoing duties. You’ll keep frameworks and dependencies up to date, monitor for vulnerabilities, and apply patches as needed. This proactive approach helps prevent security breaches and ensures compliance with data-protection regulations.
Essential Soft Skills for Success
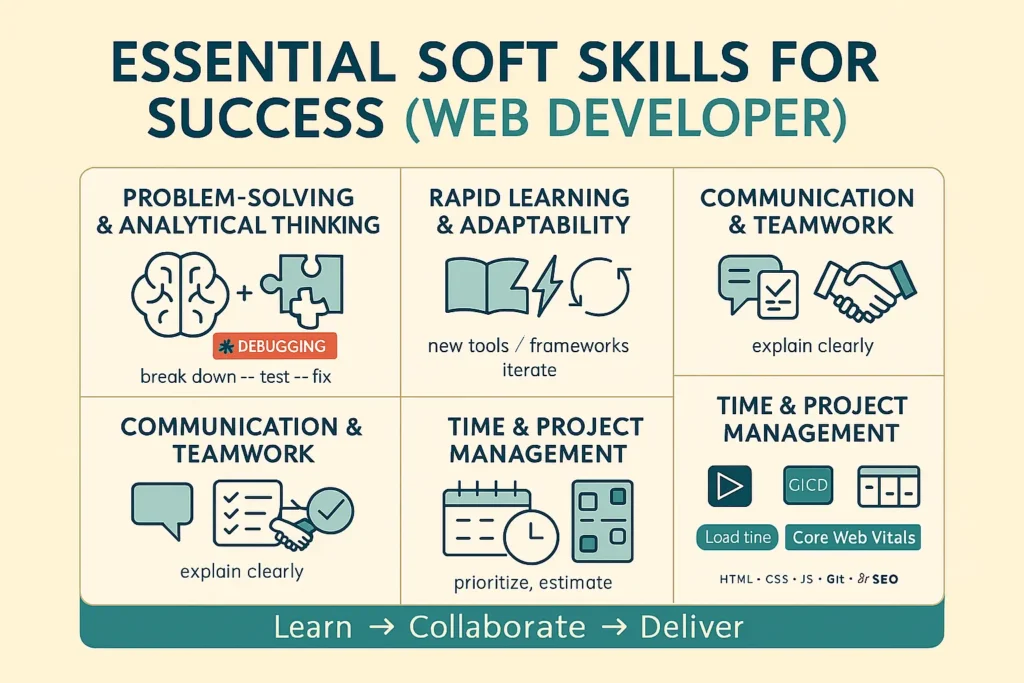
Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking
Web development is fundamentally about solving problems with code. You’ll face technical challenges daily—from debugging complex issues to optimizing performance bottlenecks. Strong analytical thinking helps you break down complex problems into manageable components and develop systematic approaches to finding solutions.
Debugging skills are particularly crucial, as you’ll spend significant time identifying and fixing issues in your code. This requires patience, attention to detail, and the ability to reason logically through cause-and-effect relationships. Effective debugging involves understanding how to use browser developer tools, reading error messages carefully, and testing hypotheses methodically.
Rapid Learning and Adaptability
The technology landscape changes quickly, with new frameworks, tools, and best practices emerging regularly. Your success as a web developer depends on your ability to engage in continuous learning and adapt to new technologies. This means staying curious, reading industry publications, participating in online communities, and experimenting with new tools and techniques.
Adaptability extends beyond learning new technologies—you’ll also need to adjust to varying project requirements, team dynamics, and client needs. Each project brings unique challenges and constraints, requiring flexibility in your approach and a willingness to step outside your comfort zone.
Communication and Teamwork Skills
Contrary to common stereotypes, web development is highly collaborative. You’ll work closely with designers, project managers, fellow developers, and clients throughout the development process. Clear communication helps ensure project requirements are properly understood and that progress is effectively conveyed to stakeholders.
Technical communication skills are especially important when explaining complex concepts to nontechnical team members or documenting your code for future use. You’ll write technical specifications, participate in code reviews, and present your work to clients and colleagues.
Time Management and Project Management
Deadlines matter in web development, where projects are often tied to strict timelines. Effective time management includes breaking large projects into smaller tasks, estimating effort accurately, and prioritizing work based on dependencies and deadlines.
Project management skills become increasingly important as you advance in your career. You’ll need to coordinate efforts among team members, manage client expectations, and ensure projects stay on track. Understanding project-management methodologies such as Agile or Scrum can enhance your effectiveness in team environments.
Work Environment and Career Paths
Available Work-Environment Options
Web development offers remarkable flexibility in work arrangements. Traditional tech companies provide collaborative office environments where you can work closely with cross-functional teams, access mentorship opportunities, and participate in company culture. These environments often offer clear career-progression paths and comprehensive benefits packages.
Digital agencies provide dynamic, project-driven settings where you’ll work on diverse projects for different clients. Agency work exposes you to a broad range of industries and technical challenges, helping you build a wide skill set quickly. The fast pace can be exciting, but it also requires strong time-management skills and adaptability.
Freelancing offers the greatest flexibility, allowing you to choose your projects, set your rates, and work from anywhere. As a freelance web developer, you’ll have full control over your schedule and client relationships. However, freelancing also requires strong business skills, self-discipline, and the ability to handle irregular income and client acquisition responsibilities.
Remote work has become increasingly common in web development, offering the benefits of employment without geographic constraints. Remote roles let you work with companies worldwide while maintaining a work-life balance. Success in remote work depends on strong communication, self-motivation, and the ability to collaborate effectively using digital tools.
Advanced Career Progression Paths
Senior developer roles are the natural step up from junior and mid-level positions. As a senior web developer, you’ll tackle more complex technical challenges, mentor junior developers, and contribute to architectural decisions. Senior roles often involve less hands-on coding and more strategic thinking about system design and technical direction.
Software-engineering roles broaden your scope beyond web development to include systems architecture, performance optimization, and large-scale application development. These positions require deeper technical knowledge and the ability to work with complex, distributed systems.
Technical-management tracks let you leverage your development experience while focusing on organizational leadership and project coordination. Engineering managers balance hands-on technical work with people management, strategic planning, and stakeholder communication.
Entrepreneurship represents an exciting path for experienced web developers who want to build their own products or consulting businesses. Your technical skills provide a strong foundation for creating web applications or launching a development agency, though success also requires additional skills in business and marketing.
Salary Expectations and Job-Market Outlook
Typical Salary Ranges Across Regions
Web developer salaries vary significantly by location, experience level, and specialization. In major tech hubs such as San Francisco, New York, and London, experienced developers can command six-figure salaries, while entry-level developers typically start in the USD 50,000–70,000 range annually. These markets offer higher pay but also come with higher costs of living.
Emerging tech markets in countries such as India, Eastern Europe, and Latin America offer competitive salaries relative to local living costs. These markets are experiencing rapid growth in technology opportunities, making them attractive to developers seeking strong career growth with lower living expenses.
Remote work has somewhat democratized salary bands, enabling developers in lower-cost regions to access higher-paying roles with companies in expensive markets. However, many companies still adjust compensation based on employee location—often at rates higher than local market norms.
Factors Influencing Compensation Levels
Your experience level strongly affects earning potential. Entry-level developers typically start with junior salaries but can expect rapid growth as they gain experience and demonstrate capability. Mid-level developers with 3–5 years of experience often see substantial salary increases as they take on more complex projects and responsibilities.
Specialization and technical skills also influence compensation. Full-stack engineers often command higher salaries due to their broader skill set, while specialists in high-demand technologies such as React, AWS, or data-driven architectures can earn premium pay. Staying current with in-demand technologies can significantly boost your earning potential.
Company size and type also shape compensation packages. Large enterprises typically offer higher base salaries along with additional benefits such as equity, while startups may offer lower base pay but meaningful ownership stakes. Consulting firms and agencies tend to pay competitively but may have different expectations for work-life balance.
Rising Demand and Future Market Opportunities
The job market for web developers continues to expand as digital transformation accelerates across all industries. The adoption of digital services has been fast-tracked by the COVID-19 pandemic, creating sustained demand for web-development skills. Traditional sectors such as healthcare, education, and retail are investing heavily in digital platforms, generating opportunities that extend beyond conventional tech companies.
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are creating new opportunities for web developers who can integrate these technologies into web applications. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), server-driven architectures, and the Jamstack ecosystem represent promising areas for developers to explore.
The freelance market and gig economy continue to grow, offering opportunities for independent developers to work on diverse projects and build successful consulting businesses. Platform-based companies at the core of the digital economy sustain demand for skilled developers capable of building and maintaining complex, large-scale web applications.
Starting Your Web-Development Career
Create a Personal Learning Plan
Beginning your journey as a web developer requires a structured learning approach. Start by identifying your career goals and preferred specialization, then create a learning roadmap that covers foundational concepts before moving on to advanced topics. Set aside consistent time for learning and practice—treat your education as seriously as a job.
Focus on building a strong foundation in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript before moving to specialized frameworks and tools. A solid understanding of core concepts will make learning advanced technologies faster and help you troubleshoot more effectively. Don’t rush through the fundamentals in favor of trendier frameworks.
Set concrete process milestones and deadlines for your learning goals. These might include completing specific online courses, building certain types of projects, or contributing to open-source repositories. Having tangible goals helps maintain motivation and provides measurable indicators of progress.
Build Projects and a Strong Portfolio
Your portfolio is your professional showcase, demonstrating your skills to potential employers or clients. Start with simple projects that illustrate core competencies, then progressively tackle more complex applications that display advanced skills and problem-solving capabilities. Quality matters most—a handful of well-executed projects is more valuable than many unfinished or poorly designed ones.
Include a variety of project types in your portfolio to demonstrate versatility. These might include a personal website, a simple web application, a responsive redesign of an existing site, and perhaps a collaborative project that shows your ability to work with others. Each project should solve a real problem or highlight particular technical skills.
Document your projects thoroughly, including the technologies used, challenges faced, and solutions implemented. This documentation helps potential employers understand your problem-solving process and technical depth. Consider writing blog posts about your projects to showcase both communication skills and technical understanding.
Keep reading and uncover secrets that can change the way you work. How to Write Programming Code Like a Pro: A Complete Guide to Excellence in Programming
Engage with the Tech Community
Getting involved in the web-development community accelerates your learning and creates valuable networking opportunities. Join local meetups, attend conferences, and participate in online communities such as Stack Overflow, GitHub, and Reddit. These interactions expose you to diverse perspectives, keep you informed about the latest industry trends, and can lead to job opportunities.
Contributing to open-source projects provides valuable experience working with existing codebases and collaborating with other developers. Start with small contributions like improving documentation or fixing bugs, then gradually take on larger features as your confidence grows. Open-source contributions publicly demonstrate your skills and show potential employers that you can work collaboratively.
Keep reading and uncover secrets that can change the way you work. How Do You Learn UX Design and Benefit From It?
Job Search and Interview Preparation
Preparing for technical interviews involves practicing coding challenges, algorithm questions, and system-design problems. Platforms like LeetCode, HackerRank, and Codewars offer practice opportunities, while mock-interview platforms help you prepare for the interview experience. Understanding common interview formats and expectations reduces stress and improves performance.
Tailor your résumé and cover letters to highlight relevant skills and projects for each application. Research companies thoroughly and come prepared with thoughtful questions that show your interest and understanding of their business and technical challenges. Demonstrate enthusiasm for learning and contributing to the success of their team.
Be ready to discuss your projects in detail, including technical decisions, obstacles overcome, and lessons learned. Practice explaining complex technical concepts in simple terms—this skill is valuable in interviews and in day-to-day work. Be honest about your level of experience while showing eagerness to learn and grow.
Keep reading and uncover secrets that can change the way you work. What Is UI and UX Design—and What’s the Difference?
Your Future in an Ever-Changing Digital World
The future of web development is bright and full of exciting opportunities. Emerging technologies such as AI, machine learning, and augmented reality are creating new possibilities for web applications. As a web developer, you’ll have opportunities to work with cutting-edge technologies that reshape how people interact with the digital world.
Staying current with technological advancements cannot be emphasized enough. The most successful developers are those who embrace continuous learning and adapt to changing demands. This means regularly updating your skills, experimenting with new tools, and understanding how emerging trends impact your work and career prospects.
The growth of the digital economy continues to create new opportunities for skilled web developers. As more businesses recognize the importance of a strong digital presence, demand for quality web-development services will keep rising. Whether you choose traditional employment, freelancing, or entrepreneurship, your skills as a web developer will remain highly valuable.
Remember that becoming a successful web developer is a journey, not a destination. Every project teaches you something new, every challenge makes you stronger, and every success builds confidence for the next opportunity. Embrace the learning process, stay curious about new technologies, and don’t shy away from projects that push your abilities.
The web-development community is welcoming and supportive, always ready to help newcomers learn and grow. Leverage this community spirit—ask questions, share your knowledge, and contribute to the collective wisdom that makes our industry stronger. Your unique perspectives and experiences will add to the rich tapestry of web-development knowledge.
Turn your goals into real achievements with our tailored services – request the service now.
Web Development: Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to become a professional web developer?
Basic proficiency in web development typically takes 6–12 months of dedicated study and practice. However, becoming truly professional requires several years of hands-on experience working on real-world projects. Timelines vary widely based on your learning speed, time commitment, and prior technical background. Consistent daily practice accelerates learning more effectively than occasional, intensive study sessions.
Can I work as a web developer without a college degree?
Absolutely. Many successful developers are self-taught or have completed alternative education programs such as coding bootcamps. The tech industry generally values practical skills and demonstrable ability over formal credentials. Your portfolio, GitHub contributions, and ability to solve real problems carry more weight than where you learned to code. That said, some large companies may prefer candidates with formal education.
What’s the best programming language for beginners?
Start with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript because they form the foundation of web development. These technologies are essential regardless of the specialization you choose later. For back-end development, Python is often recommended for beginners due to its simple syntax and gentle learning curve. However, the “best” language depends on your goals, local job-market requirements, and personal preferences.
How can I build a strong portfolio as a beginner?
Begin with personal projects that solve real problems or demonstrate specific skills. Create a personal website, build a simple web application, contribute to open-source projects, and consider redesigning existing sites to showcase your abilities. Focus on code quality, responsive design, and clear documentation. Include projects that show increasing complexity and skills over time, and be sure to explain your thought process and technical decisions for each project.